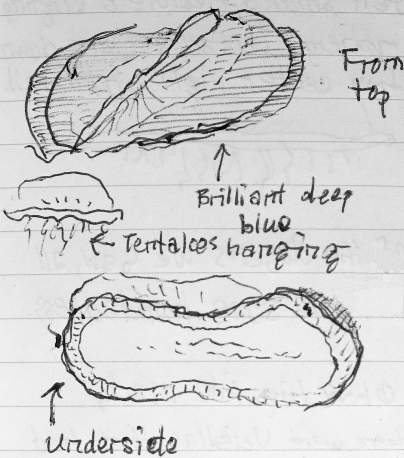
Today I was at Pescadero Marsh to look at live birds, but the dead things proved more interesting. It was just after low tide, and I saw two empty crab shells (prob. Red Crabs, Cancer productus), looking as though they had been eaten by gulls; interesting, but a pretty common sight, and it’s more interesting to actually see a gull eating a crab. Then I found the empty shells of two small crustaceans, organisms I’d never seen before. Here’s one of them:
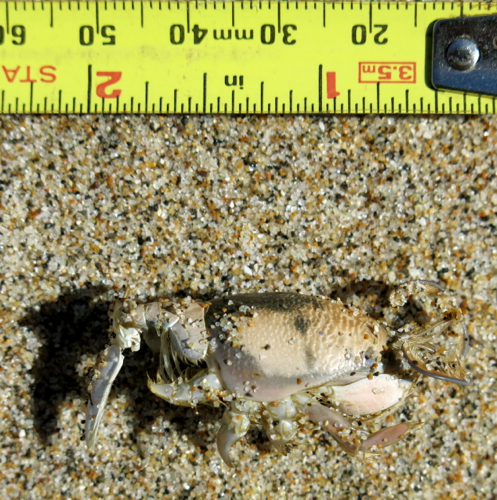

I have no idea what species this is, though I suspect it’s a fairly common organism.
Later, I walked along the dike near Butano Creek, and came across a dead mole (the notebook next to the mole is marked in inches):

Given the size of those front feet and the short tail, I’d say it was a Broad-footed Mole (Scapanus latimanus). This is the third dead mole I’ve found in six months.
What interests me when i see dead things in the field is trying to figure out how they died, and how they are tied in to the ecosystem. The Red Crabs were easy to figure out — probably eaten by gulls. But why did that little crustacean die? it didn’t look as though another organism had tried to eat it, so was it simply left high and dry at low tide? As for the Broad-footed Mole, there was a definite hole in the other side of the animal, which could have been made by a bird’s bill; I saw Red-tailed Hawks and Northern Harriers hunting in the marsh; perhaps a raptor killed the mole, then got scared away before it could eat.
These are just possible scenarios; I’ll never know what really happened; but what I do know is that somehow these dead creatures reveal something about the web of relationships between organisms.